 Reader Clytee Gold wrote me about an apparently erroneous AncestryDNA Genetic Community assignment. One of her two communities is “Mormon Pioneers in the West.” (First, I am jealous that she has two community assignments.) She is rather positive that none of her ancestors were ever Mormons. She has done extensive research and has never found any connection to the Church. As there are still pockets of prejudice against members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, this assignment could be highly offensive to some people. Coincidentally—or not—it is not offensive to Clytee. Forty years ago she joined the Church and moved to Utah. She is, literally, the “Mormon Pioneer in the West” of her family.
Reader Clytee Gold wrote me about an apparently erroneous AncestryDNA Genetic Community assignment. One of her two communities is “Mormon Pioneers in the West.” (First, I am jealous that she has two community assignments.) She is rather positive that none of her ancestors were ever Mormons. She has done extensive research and has never found any connection to the Church. As there are still pockets of prejudice against members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, this assignment could be highly offensive to some people. Coincidentally—or not—it is not offensive to Clytee. Forty years ago she joined the Church and moved to Utah. She is, literally, the “Mormon Pioneer in the West” of her family.
I’m not qualified to explain how this misassignment occurred, but fools rush in where angels fear to tread. Perhaps experts among my readers can correct me. Clytee gave one possible explanation:
The only thing I can figure out is that is based on OTHERS testing (guess that makes a community - who else took the test to compare to), and that somewhere, 5-6 generations back a sibling of a great-great something of mine joined the church in Denmark in the late 1800's and came to Utah as a "Mormon Pioneer in the west" and populated the west and there are lots of descendants who took the DNA test.
Ancestry has explained that they use an algorithm called community detection to detect groups of individuals with a large number of interconnections. I think of it like large DNA Circles that don’t require common ancestors. The Mormon Pioneers community contains 89,000 testers. Just like a DNA Circle, Ancestry states a confidence level for your membership in the genetic community. My connection to the Mormon Pioneers community is “Very Likely.”
Ancestry says they then examine the Ancestry Member Trees of the genetic community “to learn about the historical forces that may have brought their ancestors together.” Of course, some testers don’t have trees, some don’t include all their ancestors, some have ancestors without complete location information, and some have complete garbage in their trees. I assume Ancestry looks for common locations in 25-year increments. If they find a large number of ancestors who lived in the same place at the same time, they look into the history of that time period and why there was a large number of individuals there. Then they give that community a name.
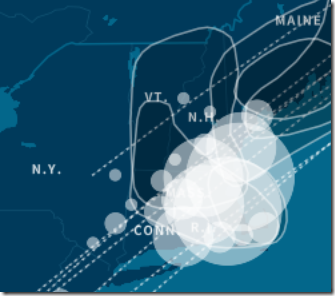
For example, the sweet spot for one genetic community is centered on Massachusetts in 1725-1750 (shown on the map, below left). Ancestry chose to name that community, “Settlers of Colonial New England.” Another centered on Utah at a much later time period, 1875-1900 (below, right). Ancestry called this one “Mormon Pioneers in the Mountain West.”

I assume Ancestry can follow the group forward and backward in time, up and down the member trees. This provides additional touchpoints to compare against historical sources and decide if they have correctly identified and named the genetic communities. Moving forward in time gives an interesting view on migration that may not be available from other demographic sources. This may truly be groundbreaking demographic tools. For example, look at the 1900-1925 map (below) of the descendants of early residents of Chihuahua and Durango. If I am interpreting the map right, by that time they were as likely to be living in El Paso as Chihuahua. (The large circle over central Texas represents ancestors whose member trees didn’t specify where in Texas they lived.)

Moving backwards in time gives an interesting view on where the Mormons who settled in Utah came from. In the period 1825-1850, most were living in England, with a fair number in Denmark. (See map, below.) The surnames associated with the Mormon pioneer genetic community further point to Denmark:
Jensen, Christensen, Larsen, Hansen, Allred, Nielsen, Olsen, Sorensen, Nielson, Rasmussen, Christiansen, Madsen, Peterson, Anderson, Barney, Leavitt, Child, Andersen, Petersen, and Jorgensen

Once they are sure they have identified the genetic community, Ancestry can take information from history books about that group and display it next to the migration map. However, the information may not apply to your ancestors who didn’t participate in the chain migration. That is how Clytee may have been put in a migratory group that her ancestors didn’t participate in. She told me her ancestry:
My father was half Swiss (4 generations from the immigrant to Missouri) and half German (5 generations from the immigrant to Missouri). Mother half Norwegian (2nd generation from the immigrant to Iowa) and half Danish (2nd generation from the immigrant to Iowa).
I think the conjunction on Denmark is more than coincidence. Clytee’s Danish ancestors didn’t have to join the Mormon church for her ancestors to share DNA with those that did. I don’t think it had to have been a sibling in genealogic-time, either. I think Ancestry is looking at shared DNA in a closed community with hundreds of years of intermarriages.
There is a possibility that the genetic community Ancestry has identified is actually more specific than “all Mormon pioneers.” Ancestry may have identified DNA of Mormon pioneers of Danish origin. Look back at the dominant surnames for this genetic community. Does it look more English or Danish?
There are other possibilities. Remember the mention of confidence level? Clytee may not belong to the genetic community at all. Her DNA may just be a statistical anomaly. Remember the mention of garbage trees? Ancestry may be running calculations overwhelmed by erroneous information.
GIGO. Garbage in—garbage out.
Thank you, Clytee, for your message.










 Over 40 years ago Glen and Joyce Alt lived in Platteville, Wisconsin where they became friends with Glenda Clyde and her husband. After several years, the two couples moved their separate ways, the Alts to Massachusetts, the Clydes to Washington state, and the couples had no further contact.
Over 40 years ago Glen and Joyce Alt lived in Platteville, Wisconsin where they became friends with Glenda Clyde and her husband. After several years, the two couples moved their separate ways, the Alts to Massachusetts, the Clydes to Washington state, and the couples had no further contact.





 Dear Ancestry Insider,
Dear Ancestry Insider,













